Forensic study about how to deal with Firearm Injuries-causes and treatment,Firearms are weapons that are capable of firing projectiles such as bullets and pellets.
- The energy to move the projectile is obtained from ignition of a propellant (eg gunpowder)
- Examples are Rifled firearm (handguns and high velocity assault rifle)and smooth bore firearms(shotgun, homemade and rubber and plastic bullets, teargas).
Also read Forensic study about how to deal with Sharp Force Injuries -causes and treatment.
Firearm injuries
- Are injuries caused/inflicted by firearms
- The characteristic of injury/wound depends on the used firearm, distance, whether it is an entry or exit wound.
Causes of firearm injuries
There are many causes of firearm injuries, the commonest are;
- War (blast war, ballistic war)
- Conflicts
- Domestic violence example robbery, kidnapping, homicide cases
- Suicide
- Ignorance of firearm use
Clinical Features of Firearm Injuries
- The most common symptoms and signs is wound, the nature of the wound will depend on whether the weapon is smooth-bore (shot gun) or rifled (gunshot).
- The characteristics of entry and exit gunshot wounds from rifled firearm can be like round to oval wound with neat edges for entry wound and irregular shape with torn edges exit wound.
Accordingly, gunshot wounds may be classified based on the presence;
- Contact wounds (less than 10mm between muzzle and skin)
- Close range wounds/near wounds (10mm-40cm in handguns and 10mm-60cm in rifles)
- Distant wounds (greater than 40cm in handguns and greater than 60cm in rifles)
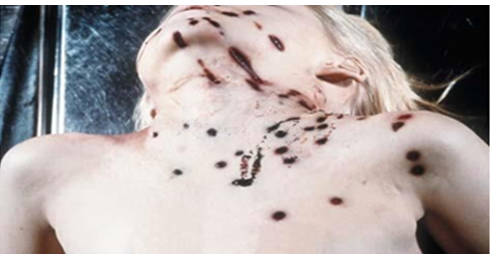
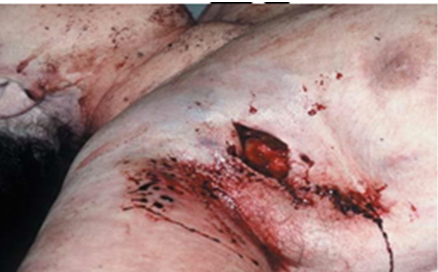
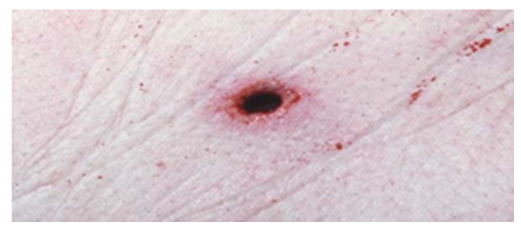
Investigations of Firearm Injuries
- Investigation process in forensic medicine involves examination of the body and laboratory, radiological (eg x- ray), pathological and others depending on the case.
- Examination will involve General, local examinations and systemic examination; general examination is concerned with looking at the whole body of the client from head to toe.
- Local examinations involve examination wounds in order to determine size, depth, nature of the wound, nature of the margins and the base.
Important information in medical legal examination about the gunshot wound;
- Number of gunshots (number of wound entry or exit)
- Type of weapon (characteristic of entry and exit wound, internal injuries)
- Range (characteristic of entry wound and firearm discharge residue)
- Direction of shot (position of entry and exit wound on body, wound track)
- Cause of death (injuries associated with wound track)
- Investigations of these injuries needs to be carefully done and documented because its findings are going to be used before the court of law.
Documentation of Findings
- All the findings should be documented properly in patient’s file and relevant legal document e.g. Police Form number3 (PF3)
Treatment of Fatal and Non fatal Firearm Injuries
Treatment of non fatal firearm injuries involves;
- Control bleeding, debridement and removal of foreign bodies (stitching if needed) , wound dressing, immobilization etc
- Ant pain/ant inflammatory injectables or tablets like paracetamol etc
- Oral antibiotics
- Tetanus toxoid vaccine
- Refer if needed.
Treatment of fatal firearm injuries involves;
- Ensure Airway, Breathing and Circulation
- Intravenous fluid like ringers lactate, normal saline
- Debridement removal of foreign bodies and control bleeding (stitching if needed) , wound dressing, immobilization etc
- Anti pain/anti inflammatory injectables
- Intravenous antibiotics as a stat dose
- Refer
Prevention of Firearm Injuries
Multi-sectorial action to prevent injuries and provide trauma care includes;
- To enforce law to minimize domestic violence
- To identify and treat mental disorders so as to prevent suicide
- Strengthen law for ownership of firearms
- Provide education on firearm use and storage for the owners of firearm.
Notification of Firearm Injuries
- Make the report as soon as possible after first becoming suspicious.
- All injuries should have Police Form number 3 (PF3) (Provide first aid management even before the availability of PF 3)
- Mandatory reporting obligations for medical practitioners in relation to suspected firearms injuries, and requires that reasonable steps are undertaken to retain projectiles or fragments taken from wounds for evidentiary purposes.
- Note: Avoid use of metal forceps to remove bullet head from the body alternatively use hand or plastic forceps for ballistic analysis.
Linkage for Continuum of Care
- A care delivery approach that links medical services, police, legal services and social support services within a confined geographic area.
- Requires a well-functioning referral system.
- Referrals within and between health facilities:
- Referrals within can be between Out Patient Department (OPD), Inpatient (IP )and
- Gender desk if available
- Referral between can be between health facilities, heath facility and Police, legal services or social welfare office if not available at the health facility.